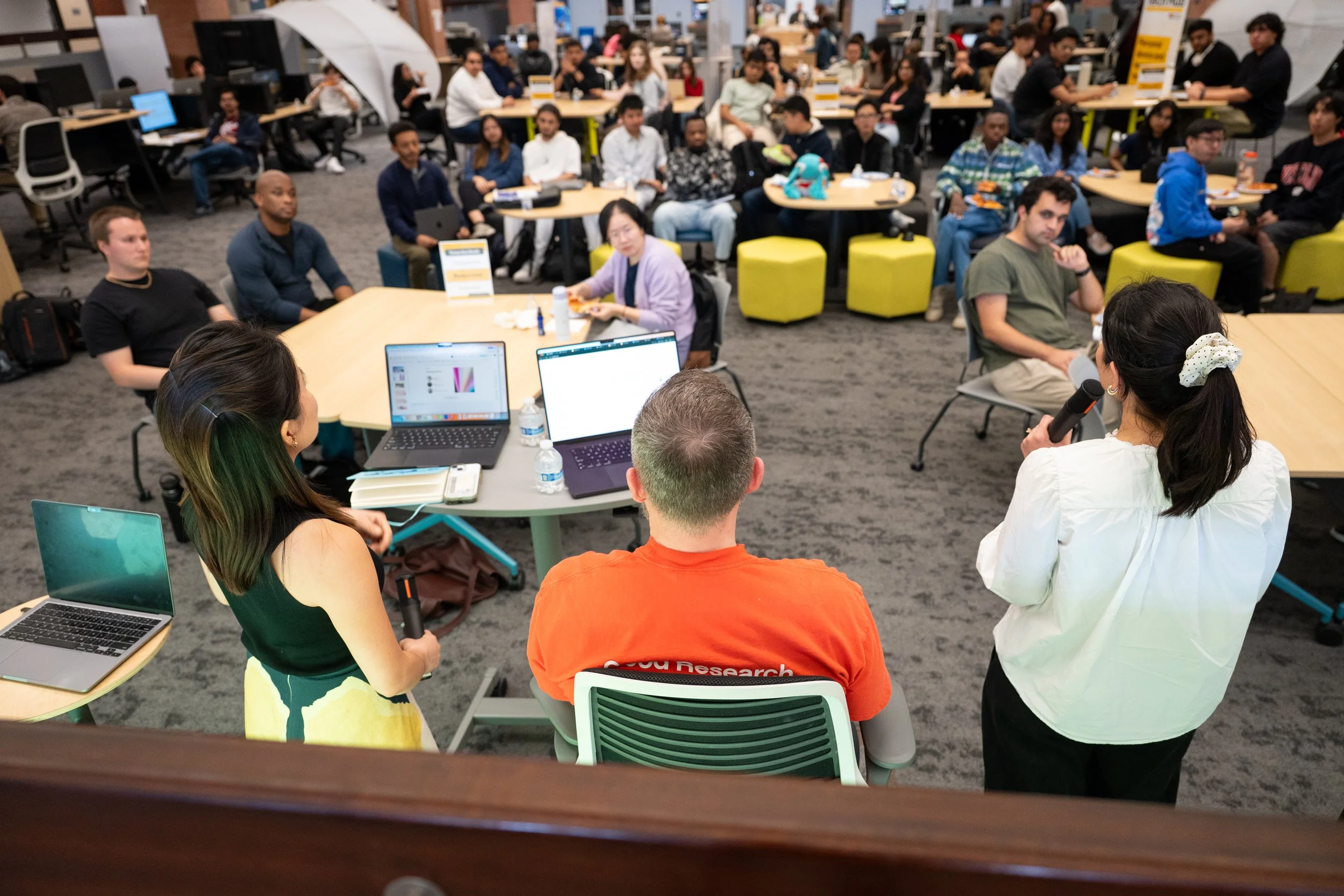
ROBOSAT researchers focus on improving autonomous machines in challenging environments
Researchers from Finland, Switzerland, Spain, and Romania joined an international workshop with the ROBOSAT project.

The ROBOSAT project aims to change how robots navigate through the use of multi-sensor and multi-GIS data.
Partners from Tampere University, ETH Zurich, Universitat de Valencia and CITST considered strategies for sharing data, identifying relevant GIS and GNSS datasets and using AI for automatic labeling of large-scale data.
The workshop covered novel technical solutions for improving the localization of autonomous machines operating in challenging environments such as mountainous regions.
Key topics covered included the integration of multi-sensor and multi-GIS data to improve positioning accuracy, planning piloting tests with ETH’s ANYmal robot, and TAU’s grabber device.
The ROBOSAT team hopes its efforts will support more reliable and precise localization for autonomous machines, allowing for improvements in robotics, environmental monitoring, and industrial automation.
Tampere University and CITST teams have already published the first dataset enabling multimodal classification studies on Zenodo.